Media refers to infrastructure and communication. What I want to explain in this section are the types of media.
The types of media in the network are divided into the following categories:
- Coaxial cables
- Twisted pair cables
- Fiber Optic Cables
Below, I'll explain each of these elements to you.
Coaxial cables
The word Coaxial in Farsi means the same axis. Currently, these cables are used in many CCTV cameras. Some of these cables have two more wires in addition to the main cable for power transmission.
Of course, the use of coaxial cables is much broader than just using it in CCTV cameras. In many cases, coaxial cables are used to transmit signals and waves, an example of which are antenna cables in residential buildings.
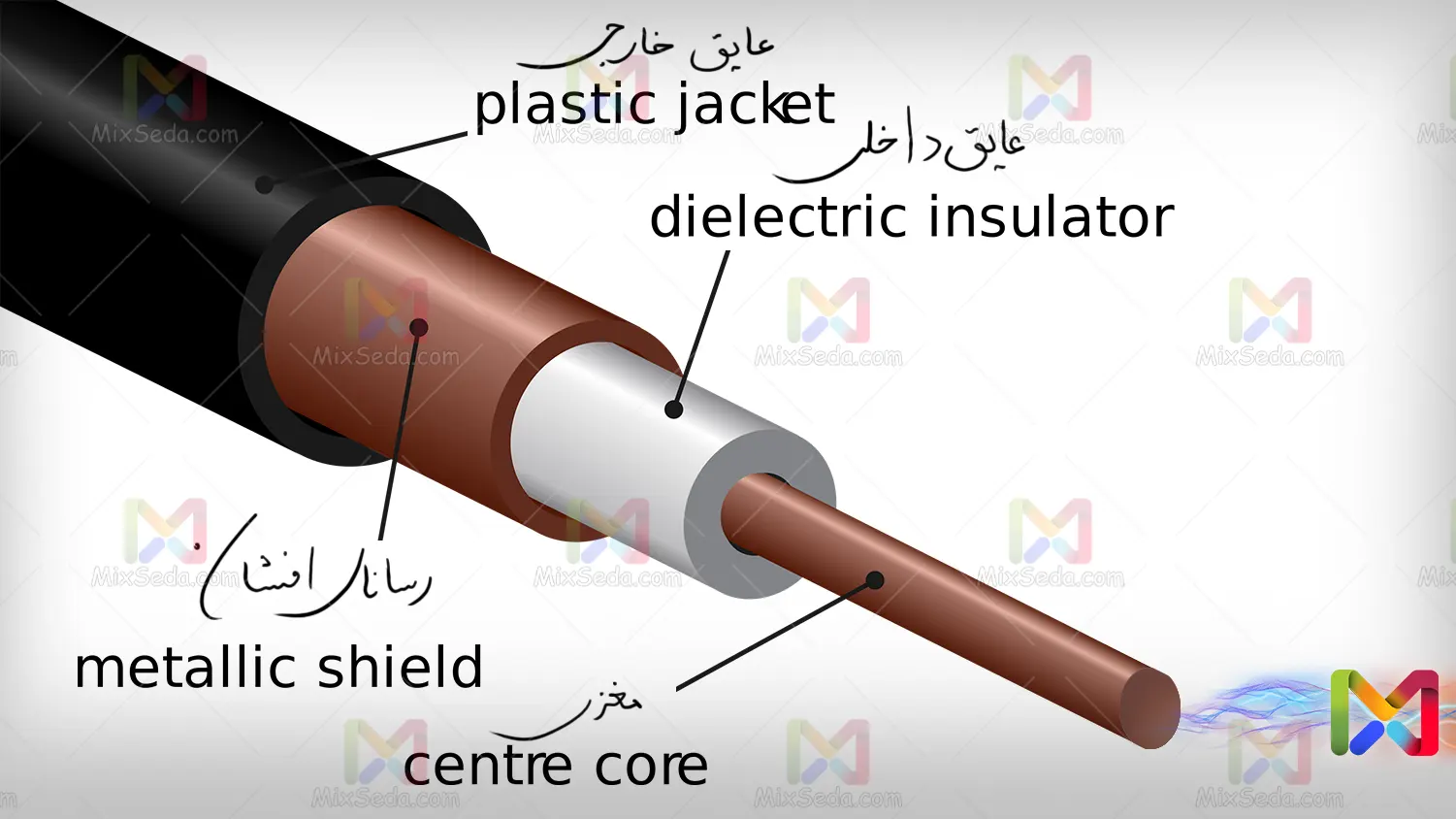
Coaxial cables consist of the following parts:
- External coating or insulation
- Director of Afshan
- Interior lining or insulation
- Nucleus
In coaxial cables, the function of the internal insulation is to prevent the connection of the conductive conductor with the core. Coaxial cables themselves also have different types based on the type of brain and the amount of signal they can pass through.
In some coaxial cables, the core itself consists of multiple cores twisted together. If you look closely, the conductive conductor is also woven quite regularly around the internal insulation. The reason for this is that external induced waves and electric fields are less likely to disturb the cable signal.
Types of coaxial cables
Coaxial cables can be classified in two ways. First of all, these cables have different types and are divided according to their type. Secondly, these cables are divided according to their impedance.
As far as I know, the types of coaxial cables are divided into the following 4 categories:
- RG6
- RG11
- RG59
- RG60
RG6 cables are used to connect televisions to central antennas and home satellites. It can almost be said that this type of coaxial cable is the weakest in signal transmission. Generally, RG6 cables are considered to be the oldest type of coaxial cables.
The RG11 cable is used in commercial buildings and large complexes. In general, this type of coaxial cable is used to transmit signals over long distances.
RG59 cables are usually used in all types of CCTV cameras. Of course, advanced cameras are usually network controlled and don't need this coaxial cable.
RG60, this type of cable is used for high volume data transmission and this type of cable has the ability to transmit the largest volume of data among coaxial cables. Some TVs that use high quality to transmit images use RG60 cables.
Coaxial cables are divided into the following two categories in terms of impedance:
- 50 ohm
- 75 ohm
In the article on the types of topologies of computer networks, we talked about the cables of Thick net and Thin net networks in BUS topology. I'm not going to repeat the same content for you here.
And I would like to remind you briefly that in thin network networks, due to the lower impedance, the maximum length of your cabling may be 185 meters, but in thick network networks, due to the presence of a higher impedance, the length of your wiring can be up to 500 meters standard. also increase.
Coaxial cable connectors
Except for some very limited cases where coaxial cables are used directly or with dedicated connectors, BNC connectors are usually used to connect coaxial cables.
These connectors themselves have two types:
Some of these connectors are pressed and used for the cable by means of special devices, but in other types the core of the coaxial cable is fixed to the connector with a screw and a metal clamp while establishing the connection with the conductive conductor; It also holds the cable.
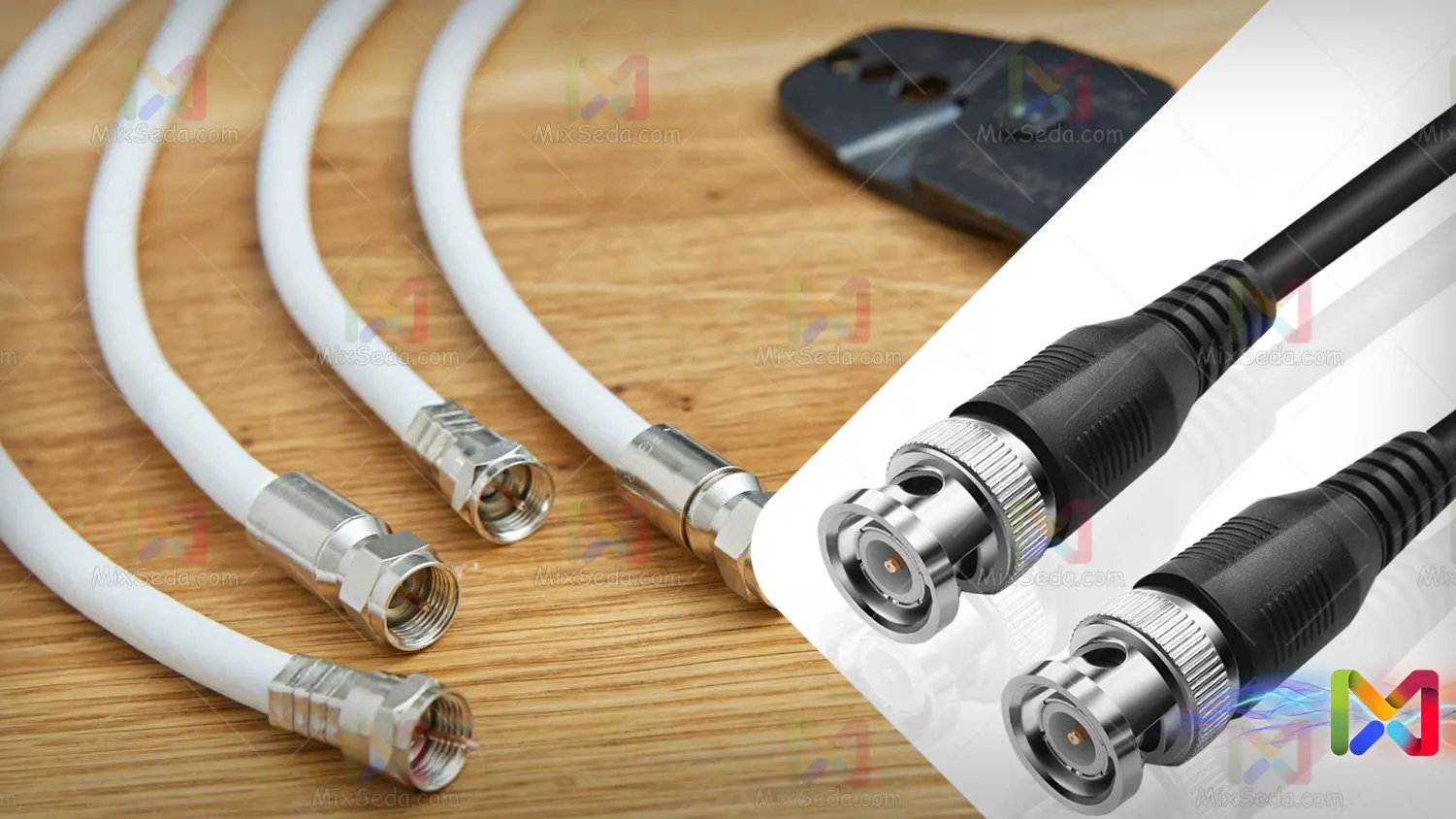

In video cameras, whose connector type is BNC type, they usually use the BNC push connector type. Also, many CCTV cameras include this type of connector.
A BNC screw connector is used on the back of TVs and to connect device antennas. Coaxial cables have the ability to transmit any type of information, but are usually used to transmit images.
Some digital audio mixers also have the ability to take audio and video signals from these connectors and work on them.
Twisted-pair cables
Twisted pair means a pair twisted together and twisted pair cables are cables that have a number of strands twisted together two by two.
Perhaps the first question that comes to your mind is why should these cables be twisted together? Indeed, these cables neutralize each other the magnetic effect. Consequently, the amount of magnetic effect created by these cables and the cables adjacent to these cables will have little effect on the signal of these cables.
Twisted-pair telecommunication cables
Twisted-pair telecommunication cables are used to transmit telecommunication data. These cables are composed of different pairs and types depending on their use.
To better distinguish these twisted pairs, a number of main standards have been defined, and in fact all cable factories produce these cables based on these standards.
For example, regarding the coloring of these telecommunication pairs, there are a series of main colors and secondary colors, which I will explain to you in the table below.
|
Row |
Original coloring |
Cable sub-coloring |
|
1 |
white |
Blue |
|
2 |
Red |
orange |
|
3 |
Black |
Green |
|
4 |
yellow |
Brown |
|
5 |
Purple |
Gray |
In twisted-pair cables, any primary color can be combined with any secondary color and radiated to each other, but you will never have the combination of two white pairs. It means that two main colors or two secondary colors are never irradiated with each other.
The following photo shows 25 twisted pairs that are produced by the color scheme in the table above:
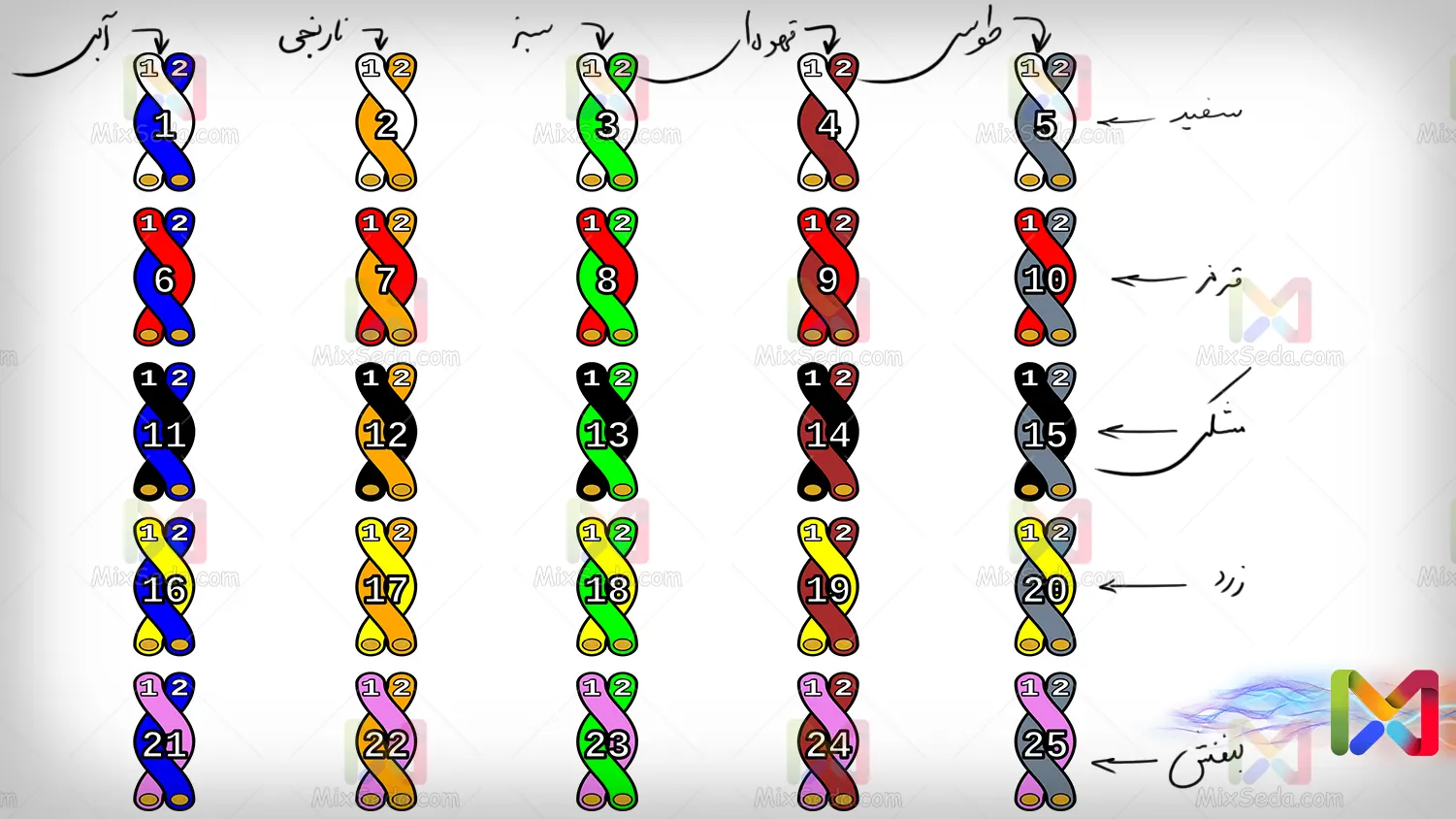

In fact, standard worldwide, the first pair of twisted pairs consists of a white and blue color scheme. Then the next pair of twisted pair cable colors is white and orange and this combination continues until the primary white color is combined with all secondary colors.
Then it is the turn of the next main color to be combined with the secondary colors one by one. The next main color is red. This means that the sixth pair of twisted pairs in the world is the red-blue color scheme.
The combination of the above colors in twisted pair telecommunication cables produces 25 pairs of cables, but the number of pairs of telecommunication cables reaches several hundred pairs in some cases. Here, what the factories that make these cables do is wrap a blue-white cover around these 25 pairs.
Then, the next 25 even numbers placed inside the cable are wrapped around a white and orange cover and so on. If this process continues 4 times, we will have 100 twisted cables and with this combination we can make 625 twisted pairs.
In most cases, the cable manufacturer only puts a colored band around the cables instead of a cover. Because practically the presence of a colored band can determine the category of cables and there is no need for a cover.

Telecommunication cable sockets
4P2C RJ9 Connector
These connectors are usually used to connect phones. Generally, a twisted pair is connected to this type of connector.
4P4C RJ9 Connector
In the case of switchboards and telephones connected to switchboard devices, these connectors are usually used. Two twisted pairs are connected to this connector and in the telephones, in addition to the main signals, other data is also transmitted through the other pair.
In some cases, this type of connector is also used to connect some ADSL and VDSL modems. Of course, this depends on the type of wiring in the building.
6P4C RJ11 Connector
This type of connector is exactly the same as the 4P4C RJ9 connector, except that in this type of connector you will have two blank pins. In practice, these two connectors will have no difference from each other and the only difference lies in their design format.
6P6C RJ11 Connector
In many cases, this connector is not used for telecommunication cables. This connector has the ability to connect three pairs of wires and is used for very few tasks.
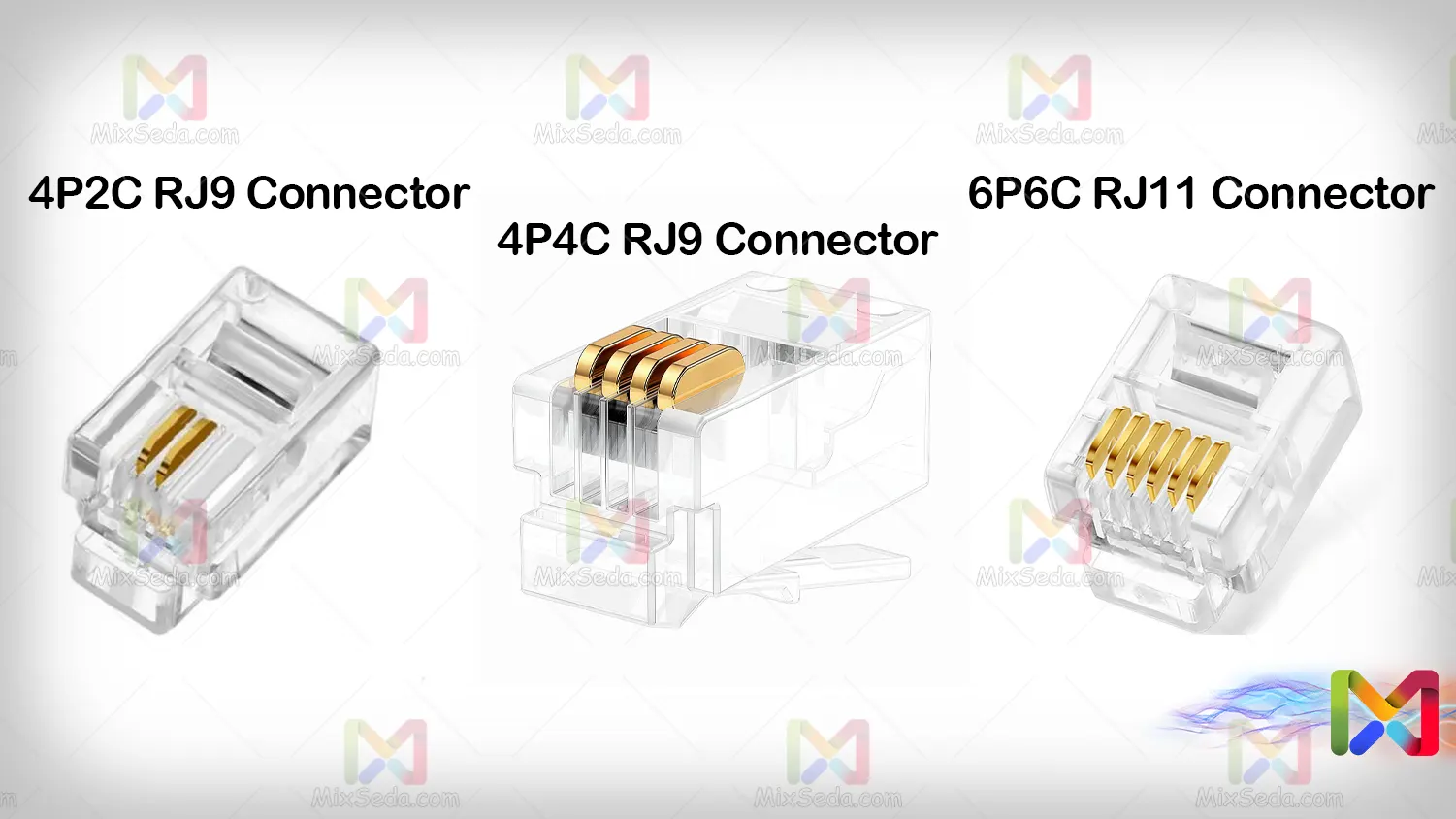
In the standards you see in the image above, you may have noticed the meaning of P and C. 6P means that this connector has 6 parts to place the pin and 4C means that of these 6 parts, only 4 metal parts are found for connecting to the wire and connector.
Twisted-pair cables in the network
The twisted pairs in the network are the same as the twisted pairs in telecommunication cables, except that the colors of these cables are different. These cables have 4 pairs twisted together. The color of these cables is such that the white color is combined with 4 secondary colors and each of these 4 secondary colors is repeated once.
|
Row |
Composition |
The result of the combination |
|
1 |
Main color white + secondary color blue |
White-blue |
|
2 |
Blue secondary color |
Blue |
|
3 |
Main color white + secondary color orange |
White-orange |
|
4 |
Orange subcolor |
orange |
|
5 |
Main color white + secondary color green |
White-green |
|
6 |
Green secondary color |
Green |
|
7 |
White main color + brown secondary color |
White-brown |
|
8 |
Brown undertone |
Brown |

Structure of twisted-pair cables
The same twisted-pair cables in computer networks have different types based on the type of structure:
- UTP
- STP
- FTP
- SFTP
The letters TP at the end of each of the above types are short for twisted-pair words. Below, I'll give you a brief explanation on each of these types:
UTP
Unshielded UTP or twisted pair network cables are unshielded cables. In fact, these types of cables have no protection or shielding around the cable, and the only protection is the plastic shell of the cable itself.
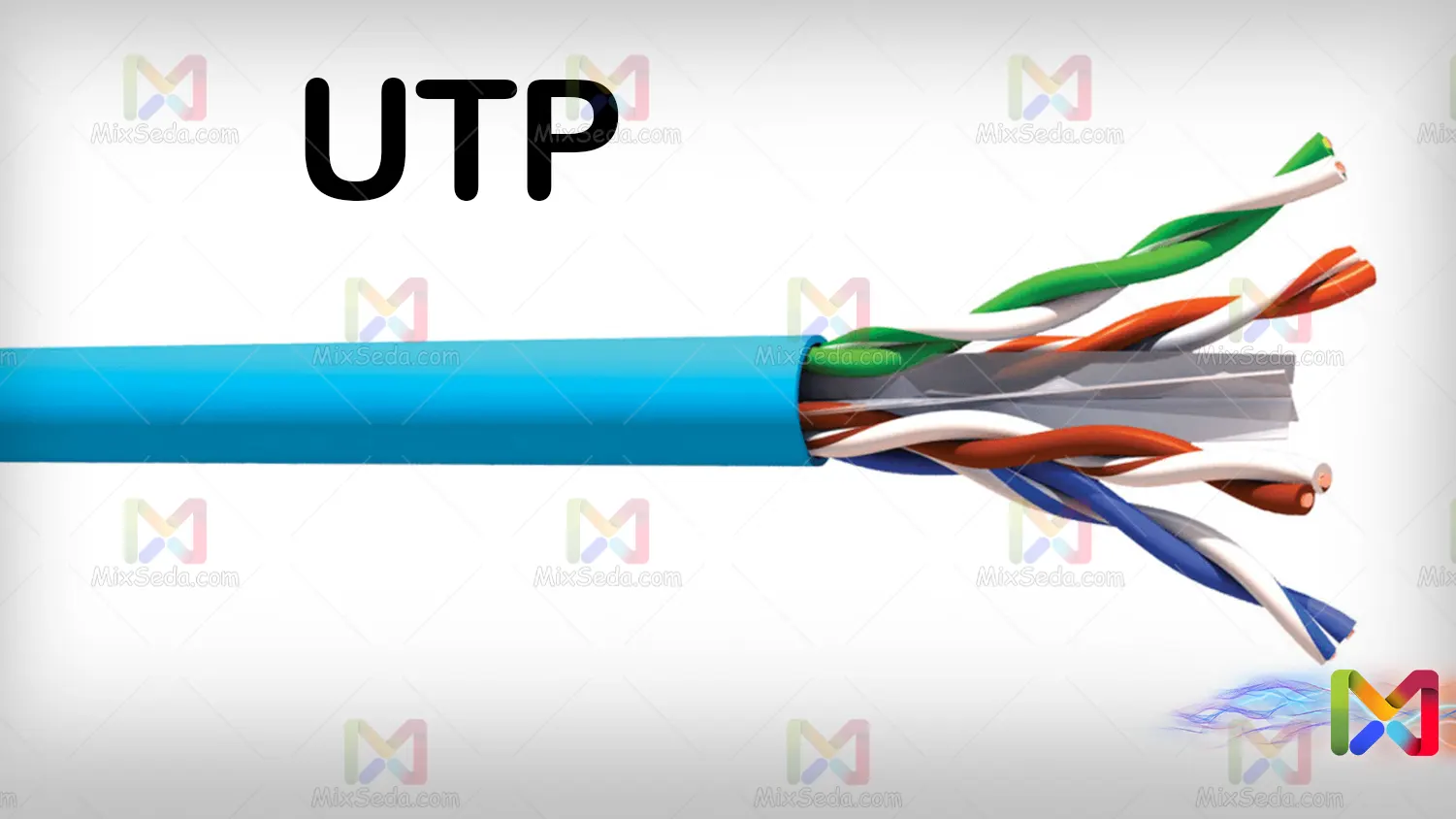
These cables are usually used in places where there is no noise and magnetic induction. As these cables do not have any kind of protection and running a power cable next to these types of cables can easily cause noise in the network.
STP
Unlike UTP cables, STP or shielded twisted-pair cables have a braided shield around the wire, which increases the resistance of the wire and reduces the effect of magnetic induction of other cables on this type of cable.
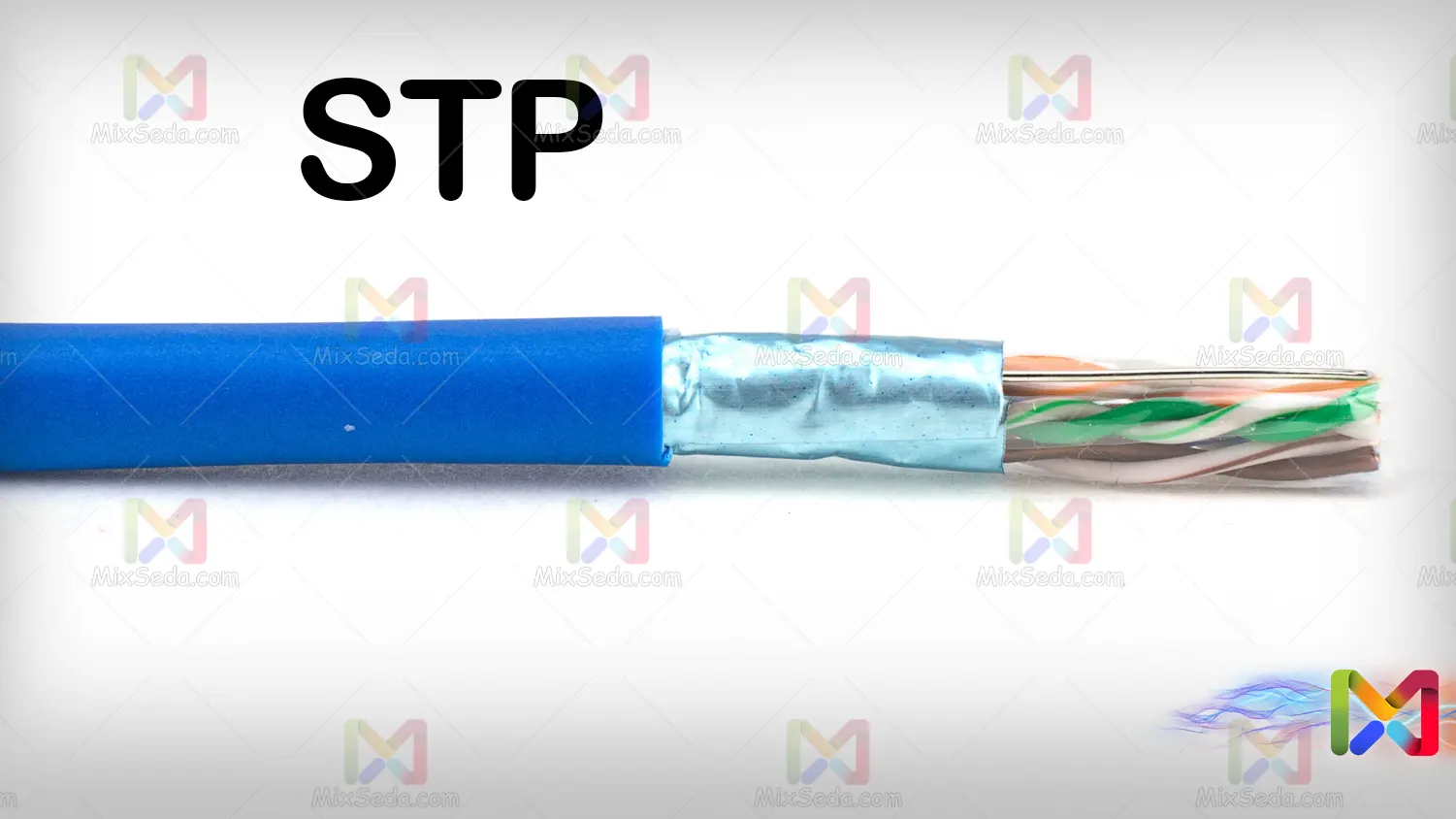

Of course, we don't discuss cable resistance much in the network discussion, and most of our priority is to use equipment to reduce noise. Surely, if you do standard wiring, you shouldn't worry too much about the resistance of the wires because these wires pass through the conduit and nothing will damage them.
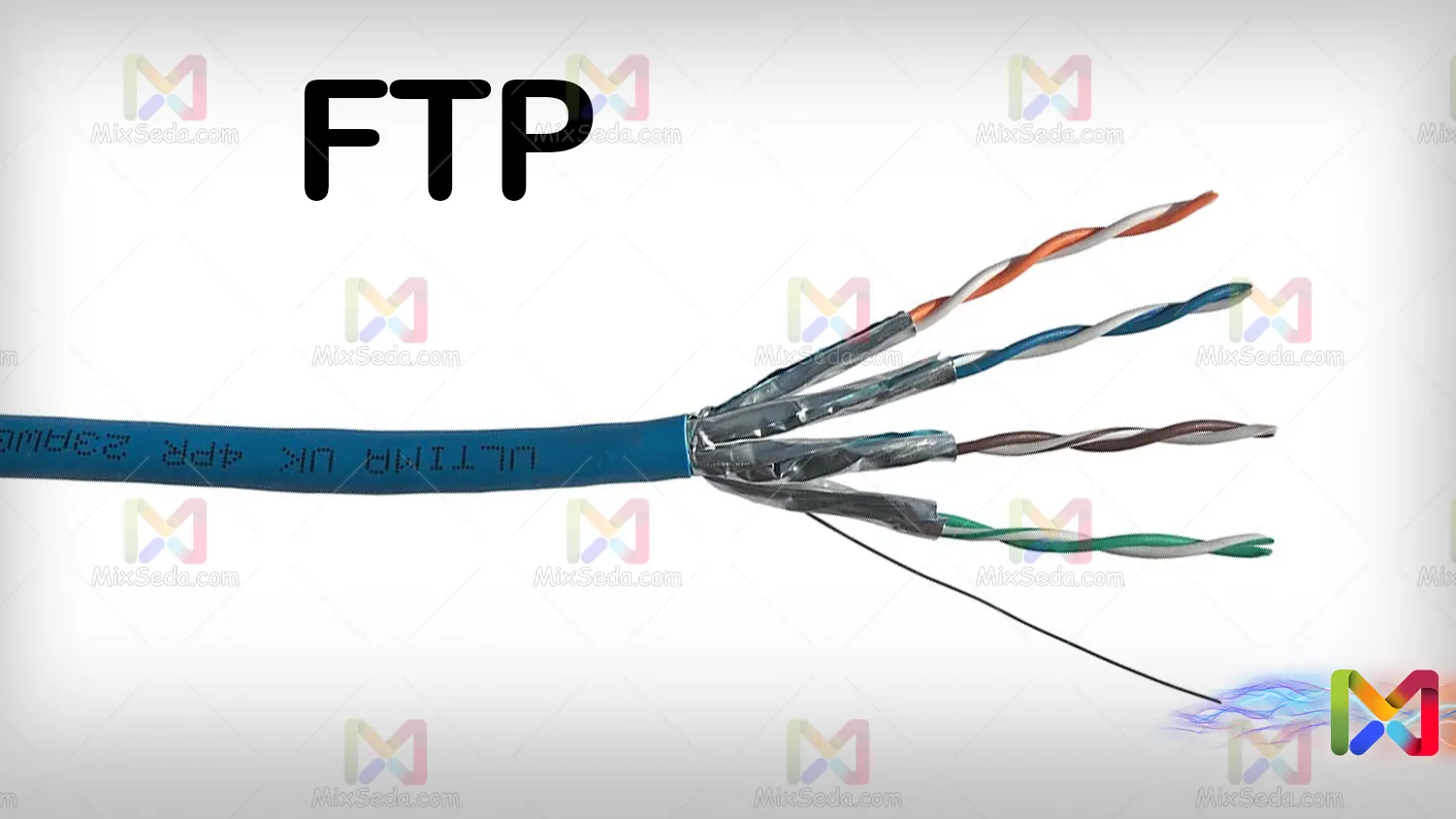
FTP
FTP or twisted-pair cables are cables that have foil wrapped around each pair of cables to reduce the amount of noise created by the magnetic induction of other pairs. In fact, this foil protects each pair from other pairs of cables.
SFTP
SFTP or shielded twisted-pair cables are cables that, in addition to the shield, also have a foil wrapped around each pair. These cables are thicker than other types of network cables and are not easily flexible. Also, connecting the connector to this type of wire is a bit more difficult than with UTP cables.
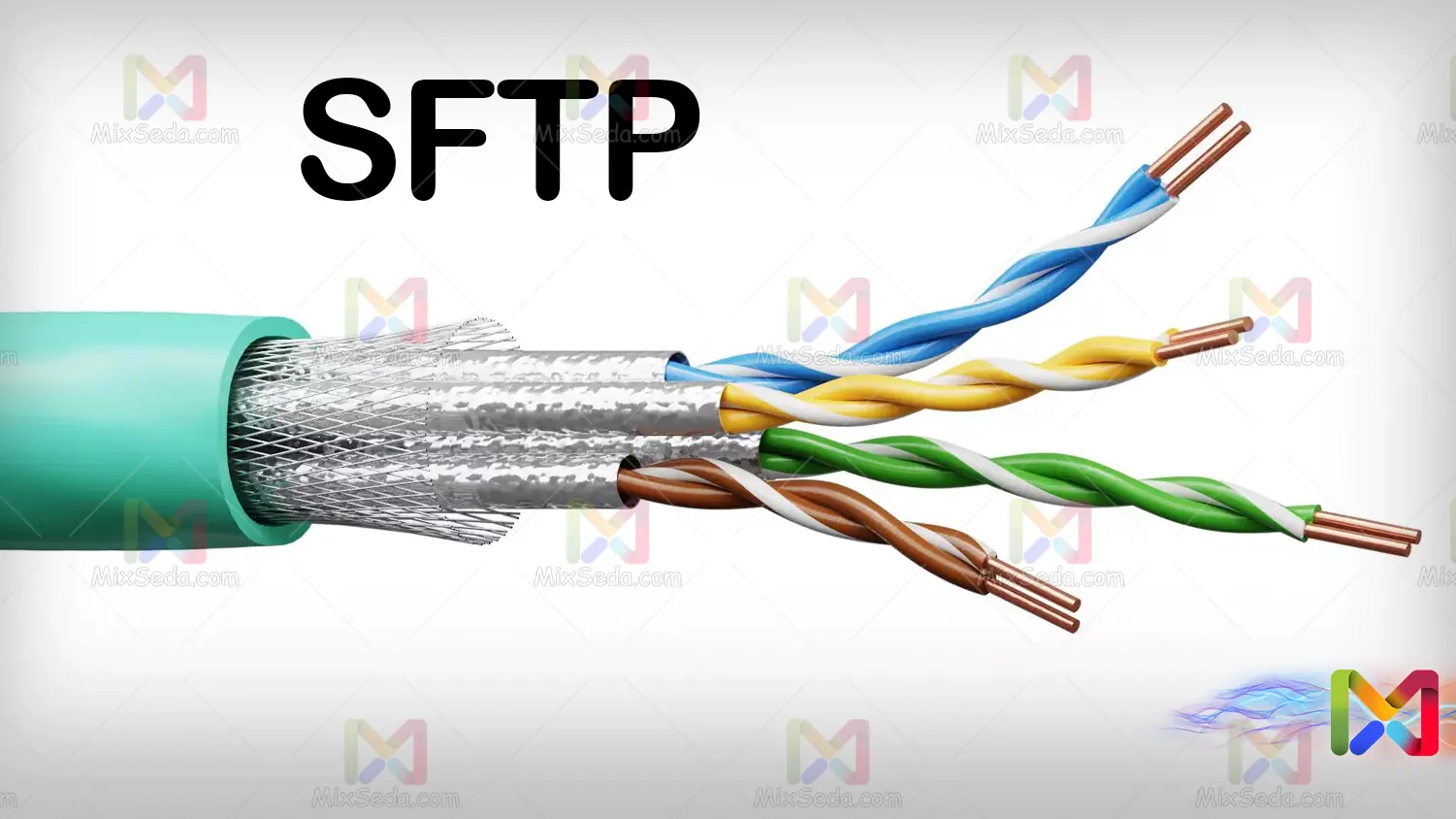
But in terms of durability and performance, this type of cable is much better than UTP. Usually, they try to use these cables in places where access is more difficult, because less noise affects the data passing through these cables and also these cables are more durable than other network cables.
These four types of cables that we have explained above are also classified by manufacturing factories based on the material used in the artifact and the type of component placement. Perhaps you will come across cables that consist of multiple layers.
Usually, these products are custom made and there is no global and international standard defined for them. For example, if you are looking for double shielded cables on the internet, you will definitely see them.
Classification of network cables based on category
In addition to the type of structure that network cables have and by which they are classified, we also learn about another concept called category or CAT in network cables. Category is a category of network cables that determines the maximum amount of cable bandwidth in networks.
The higher the CAT number written on a network cable, the more the wires of the cable are stacked and with this number also increases the data exchange rate and the amount of data the cable can transfer in one second. I have prepared the specifications of these categories for you in the following table.
|
Row |
UTP category |
Data Rate |
Max. Length |
Cable Type |
|
1 |
CAT1 |
Up to 1Mbps |
- |
Twisted pair |
|
2 |
CAT2 |
Up to 4Mbps |
- |
Twisted pair |
|
3 |
CAT3 |
Up to 10Mbps |
100m |
Twisted pair |
|
4 |
CAT4 |
Up to 16Mbps |
100m |
Twisted pair |
|
5 |
CAT5 |
Up to 100Mbps |
100m |
Twisted pair |
|
6 |
CAT5e |
Up to 1Gbps |
100m |
Twisted pair |
|
7 |
CAT6 |
Up to 10Gbps |
100m |
Twisted pair |
|
8 |
CAT6a |
Up to 10Gbps |
100m |
Twisted pair |
|
9 |
CAT7 |
Up to 10Gbps |
100m |
Twisted pair |
|
10 |
CAT8 |
Up to 40Gbps |
30m |
Twisted pair |
Of course, CAT1 to CAT4 cables are no longer used in computer networks and are actually obsolete. CAT1 cables were used in old telecommunication networks for old phones. CAT2 cables have also only been used in token ring network topologies in the past.
Maybe the above table raises the question for you, what's the difference between CAT6 and CAT7 cables?
CAT6 and CAT6a cables have a transmission power of 10 Gbps only up to 55 meters in length. Meanwhile, CAT7 cables up to 100 meters can transfer this amount of data per second.
Network cable connectors
The only connector used to connect network cables is the RJ-45 connector, which in turn has different designs based on the material and type of metal used and these connectors are usually based on the type of network cable used. the category is linked to it will be classified.
As for connecting cables to this type of connector, there are two types of colors, known as T-568A and T-568B. Of course, the T-568B standard is usually used in computer networks. You can see them in the photo below:
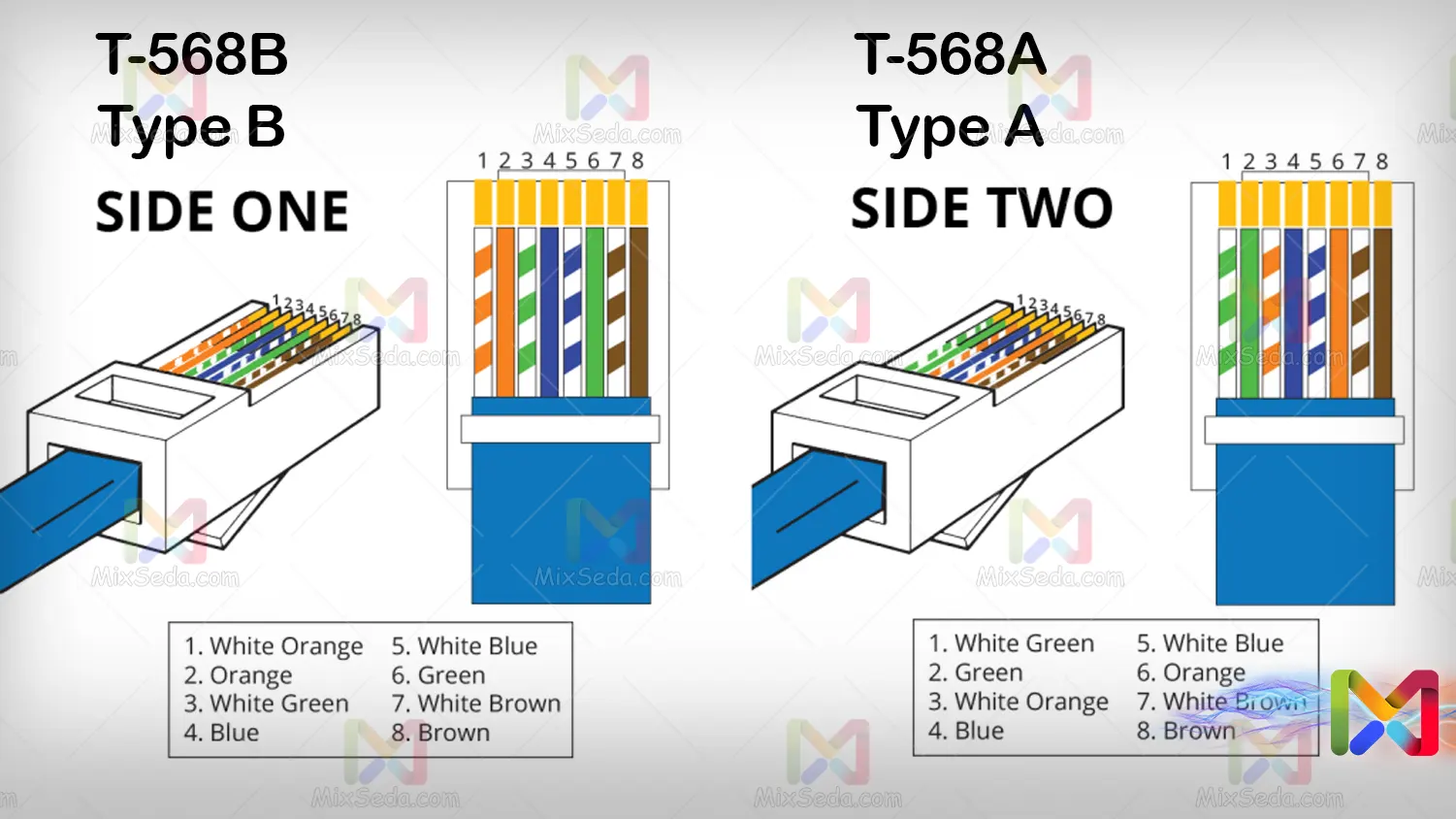
You may be wondering if other colors cannot be used to connect these cables?
In fact, you can use any color you want for your network cables. But if you don't use these standards, two problems may arise for you:
- Usually these standards are designed in such a way that the least amount of noise affects your network. If you don't use these standards, you may notice a lot of noise on the network.
-You are not always in charge of a network. After some time, another person may want to work on your network. In this situation, he should be able to easily do the wiring he needs by knowing these standards.
Connect the connector to the network cables
You may see two types of network cables in your computer networks.
Crossover
A crossover network cable is when one of the network cable connectors is connected as T-568B and the other cable connector is connected as T-568A. Of course, this type of cable is not common now and in the past they were used to connect two computers or two switches together.
Straight
Straight cables are cables with both ends of the RJ-45 connectors connected such as T-568B or T-568A. This means, for example, that you have a cable with Rj-45 connectors connected to the standard T-568B on both ends of this cable.
This type of cable is used to connect switches to computers. Currently network cards are smarter than ever and you connect any type of cable to any device, the network card itself recognizes the type of cable and you will not encounter any problems connecting cables.
Fiber optic cables
Fiber optic cables are the fastest cables for data transmission. These cables have a much higher speed than other network cables. Also, the cost of network implementation using these cables is much higher than with other cables.

Among the advantages of fiber optic networks we can mention:
- high security
- noise immunity
- low weight
- High bandwidth
- High transfer speed
Additionally, fiber optic cables have fewer cabling restrictions. In fiber optic cables, due to the existing structure, we cannot easily connect them together. The fiber optic cable connector is a device called Fusion, which for us does it easily.
Types of fiber optic cables
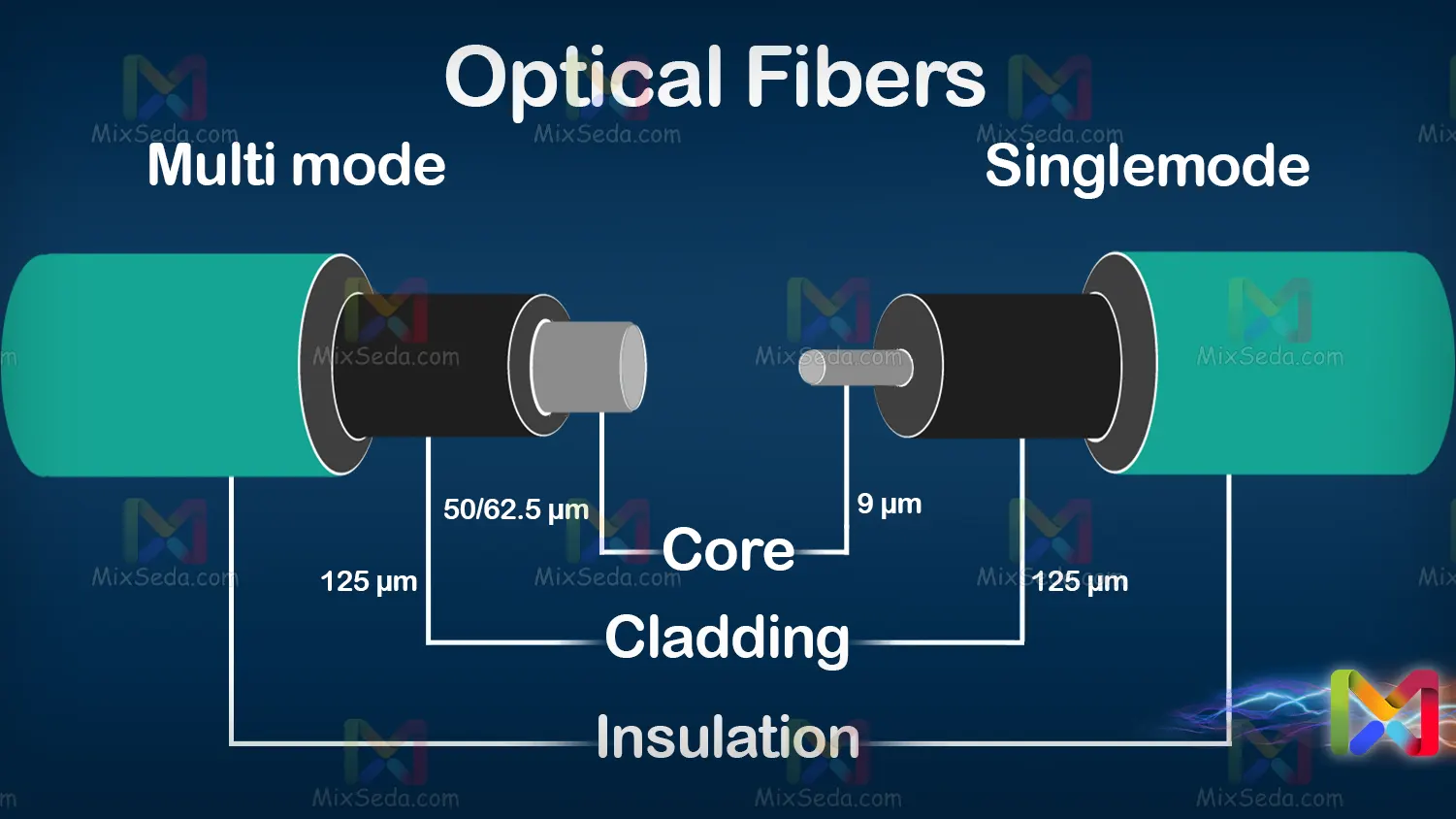
There are two different types of optical fiber cables, and we will examine each of them below:
Single mode
The core of these cables is smaller than multimode cables. So that the diameter of this core in singlemode fiber optic cables is between 8.3 and 10 microns. The bandwidth of singlemode cables over long distances is more than multimode.
But for this type of fiber optic cable it is necessary to use a light source with a narrow spectrum. This means that a laser must be used for this type of fiber optic cable. The cost of implementing the network using singlemode cables is lower than multimode.
But these cables have the power to transmit your information up to 80 kilometers. Also, since the light inside this type of fiber optic cables only moves directly, the transmission speed of these cables is also higher than in the Multi mode.
Multi mode
This type of cable has a thicker core and the diameter of this core is between 50 and 100 microns. You can transfer up to 400 meters of data using this cable. Also, this type of cable has more applications due to its lower cost than singlemode cables.
For example, in many data centers and office complexes, this type of cable is used for data transmission because both its cost is lower and you won't have more than 400 meters of cabling in the complexes. Furthermore, the light source of this type of fiber optic cable does not necessarily have to be a laser and LEDs can also be used for this type of cable.
If you intend to use multimode fiber optic cables over long distances, you need to use devices called repeaters, which are expensive to use.
What repeater devices do is reproduce the signals and waves of a cable. Note that these devices reproduce waves and do not amplify the waves already generated.