basic concepts
Before you want to familiarize yourself with the concept of topology and the topology types of computer networks, you need to familiarize yourself with a number of basic concepts. Next, I'll explain each of these concepts:
Host
Guest means guest. A very important point in the specialist lessons is that there is no attempt to use the translated equivalent of the words. In the future, you need to be able to interact with your colleagues in job interviews, and memorizing the translated words could lead you astray.
Any computer system that can analyze data or store it is called a host. Of course, we don't mean a computer system, a device with a mouse, keyboard, etc. A mobile phone that has the ability to analyze data is considered a host.
By default, any laptop, computer, server, or any other device that can analyze or store data for you is considered a host.
Workstation
Computer systems that are connected to a network and use network resources are called workstations. If we want to look at the matter more simply, the hosts that use network resources in your network are called workstations. A printer can act as a workstation on the network.
Topology
Imagine that you have been provided with a host of hosts and intend to design a computer network using these hosts. The first thing that might come to your mind is how these hosts should connect to each other. This is exactly the concept of topology in the network.
Topology is actually how network elements are physically connected. Maybe your idea of physical connection is a little different. The topology does not indicate the type of cable used. In effect, network topologies are communication structures used to network computers.
Below, we will evaluate each of the network topologies and explain the advantages and disadvantages of each of these topologies for you loved ones.
Examining types of topologies
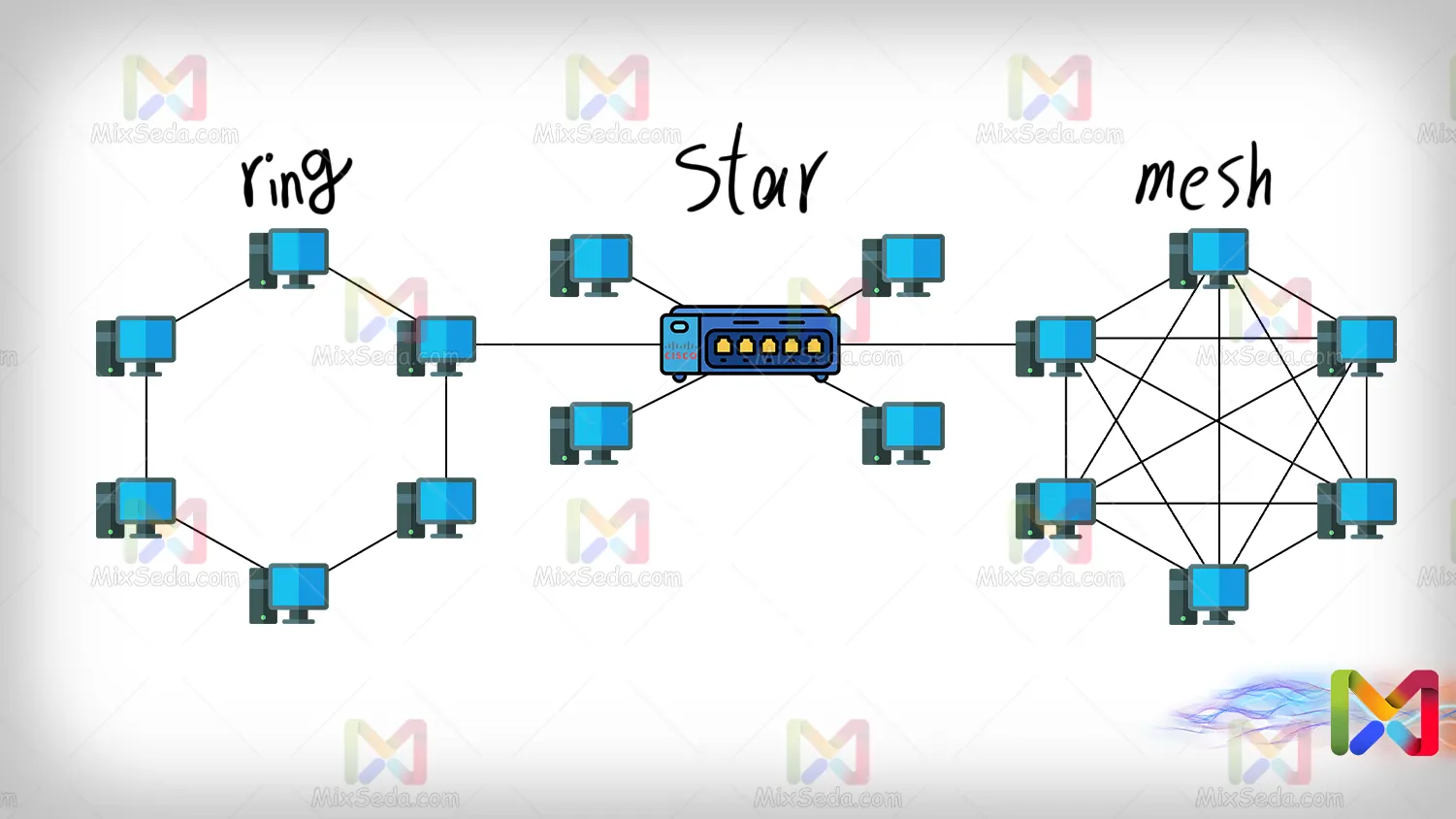
Ring
Ring topology, as the name suggests, is created by connecting computer systems in a ring. In the ring topology, as can be seen in the following figure, for a packet to reach destination E from source A, it must pass through several computers.
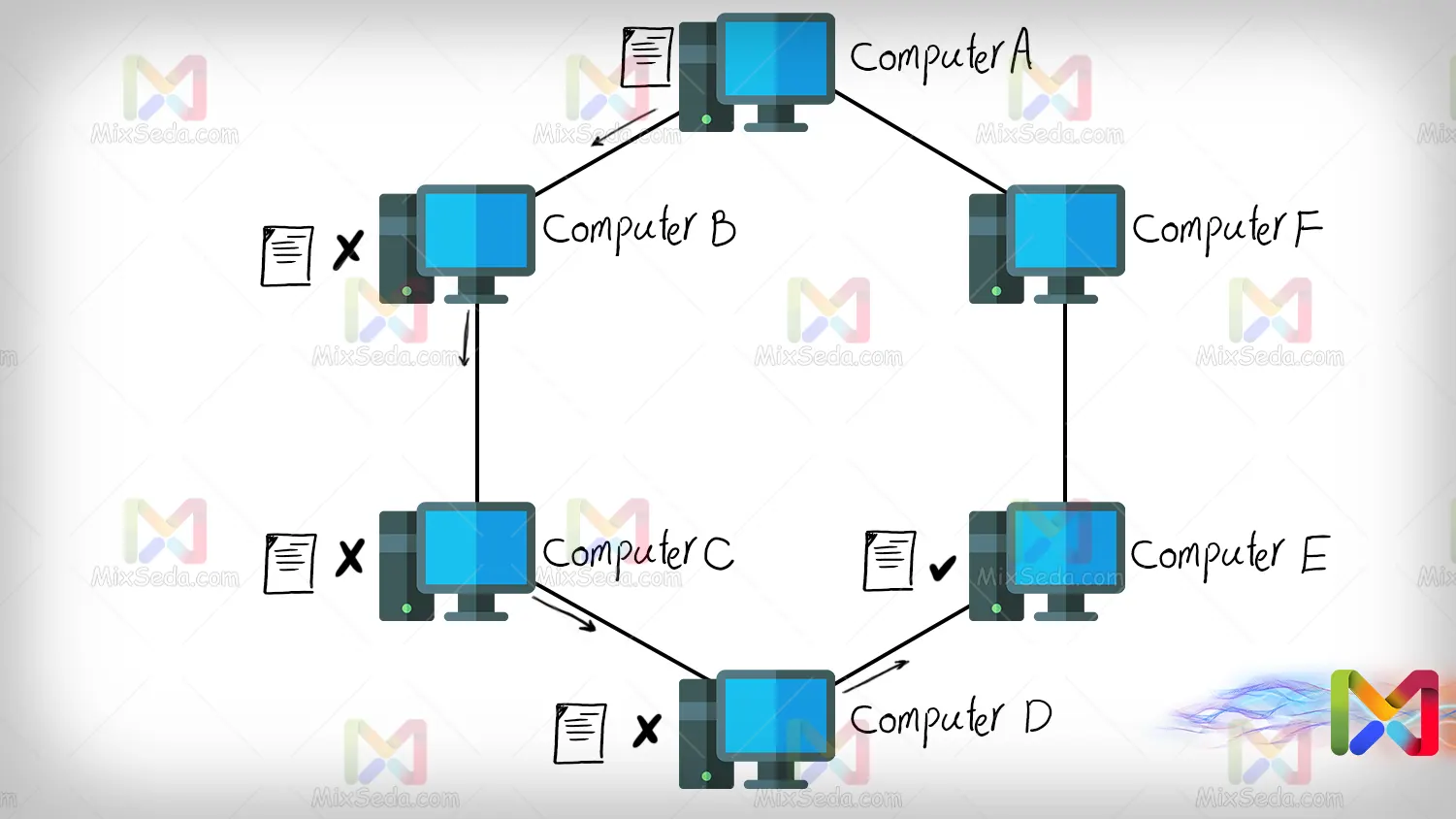
For example, if computer A intends to send a packet to destination E, this packet will also pass through computers B, C and D. In fact, what happens here is that these computers drop it when they realize that the packet being sent is not it is related to them.
In the Ring topology, packets do not continue to rotate and pass continuously between computers, but after reaching a point in the Ring, regardless of whether or not they have reached the desired destination, they are discarded.
The following are the advantages of the ring topology:
- The cabling length of this topology is less than other topologies.
- The cost of using this topology is lower and it is among the cheap topologies.
Of course, this topology has many disadvantages. For example, if one of these computers goes off the network for any reason, access to other computers becomes impossible. In terms of security, networks using this topology had a very low security level.
Another disadvantage of this topology is the troubleshooting of such networks. Suppose the cable between two computers is unable to transfer data for any reason. In your network, you need to strive to notice the desired cable failure. It will also be difficult for you to update these networks.
Adding more computers to these networks can take a long time. To add some computers to the network, it may be necessary to disconnect the old network for some time to connect new connections to the computers you plan to add to the network.
Mesh
In networks using mesh topology, each network component is connected to each other separately. You can see an example of this network in the image below.
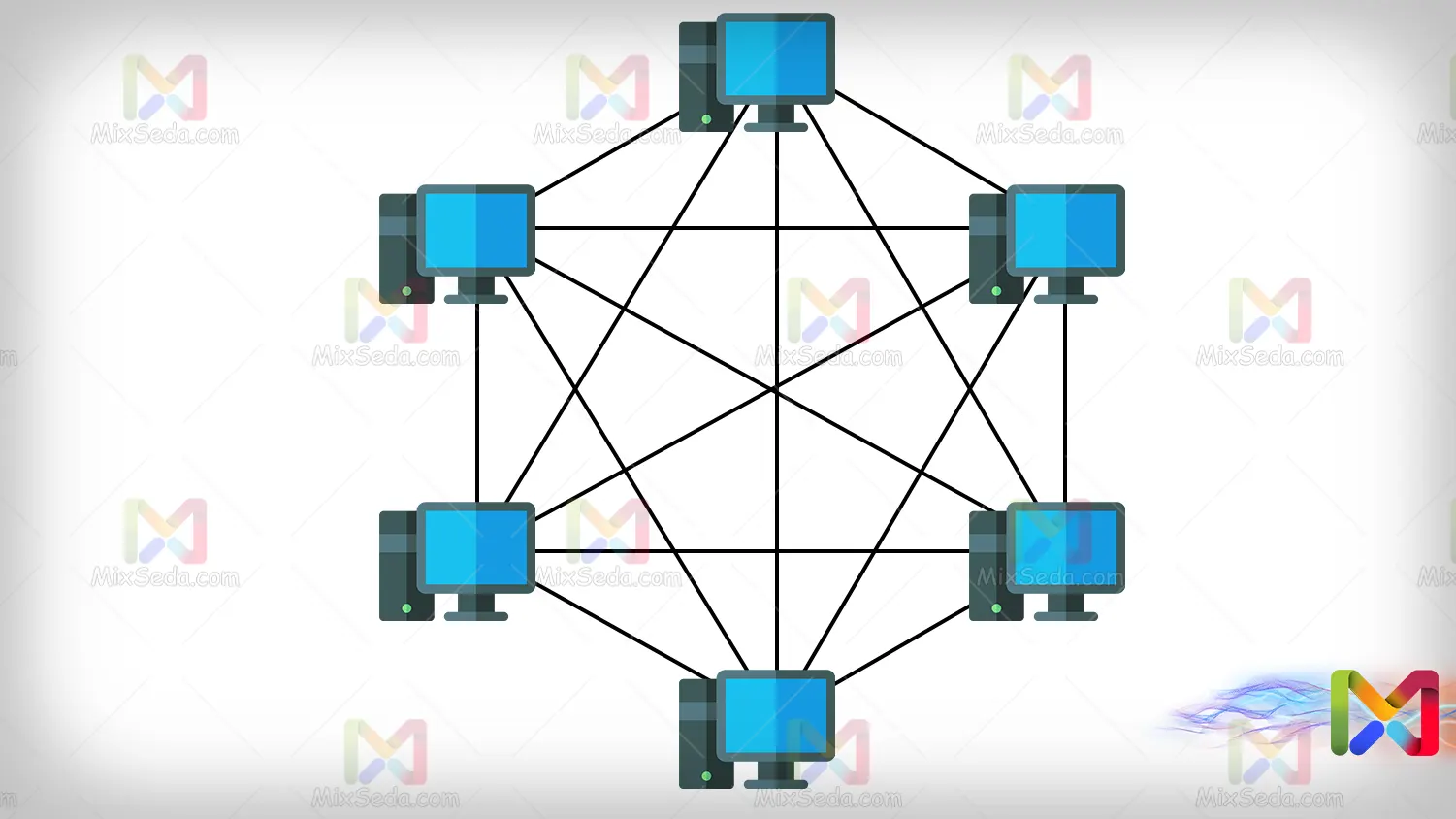
In networks using mesh topology, when a computer is disconnected, the computer's network is not disconnected. That is, what happened in ring networks when a computer is disconnected does not happen in these networks.
Also, if a cable is unable to transfer data to the destination, only the connection between the two computers will be broken. Troubleshooting these networks is also much easier than networks that use the ring topology.
As for the disadvantages of these networks, what is very clear at first glance is the amount of cabling between the computers. Suppose we want to add another computer in the same image above; For this, you need to get as many cables as there are computers in your network.
That is, if I want to add the seventh computer to my network, I have to prepare six cables to connect this computer to other computers in my network. In fact, the formula for calculating the number of cables connected to each computer on the network is "n-1", where n is the number of computers on your network.
When the amount of cabling of a topology is high, the cost of implementing that topology will be high. Therefore, the use of mesh topology is very expensive, especially in large networks.
On the other hand, it is very difficult to expand networks that use this topology for data transmission.
Bus
The BUS topology is one of the obsolete topologies that almost as far as I know no one uses this topology anymore. In this topology, the coaxial cable is used for the implementation. Today, coaxial cables are used to transmit images and connect CCTV cameras.
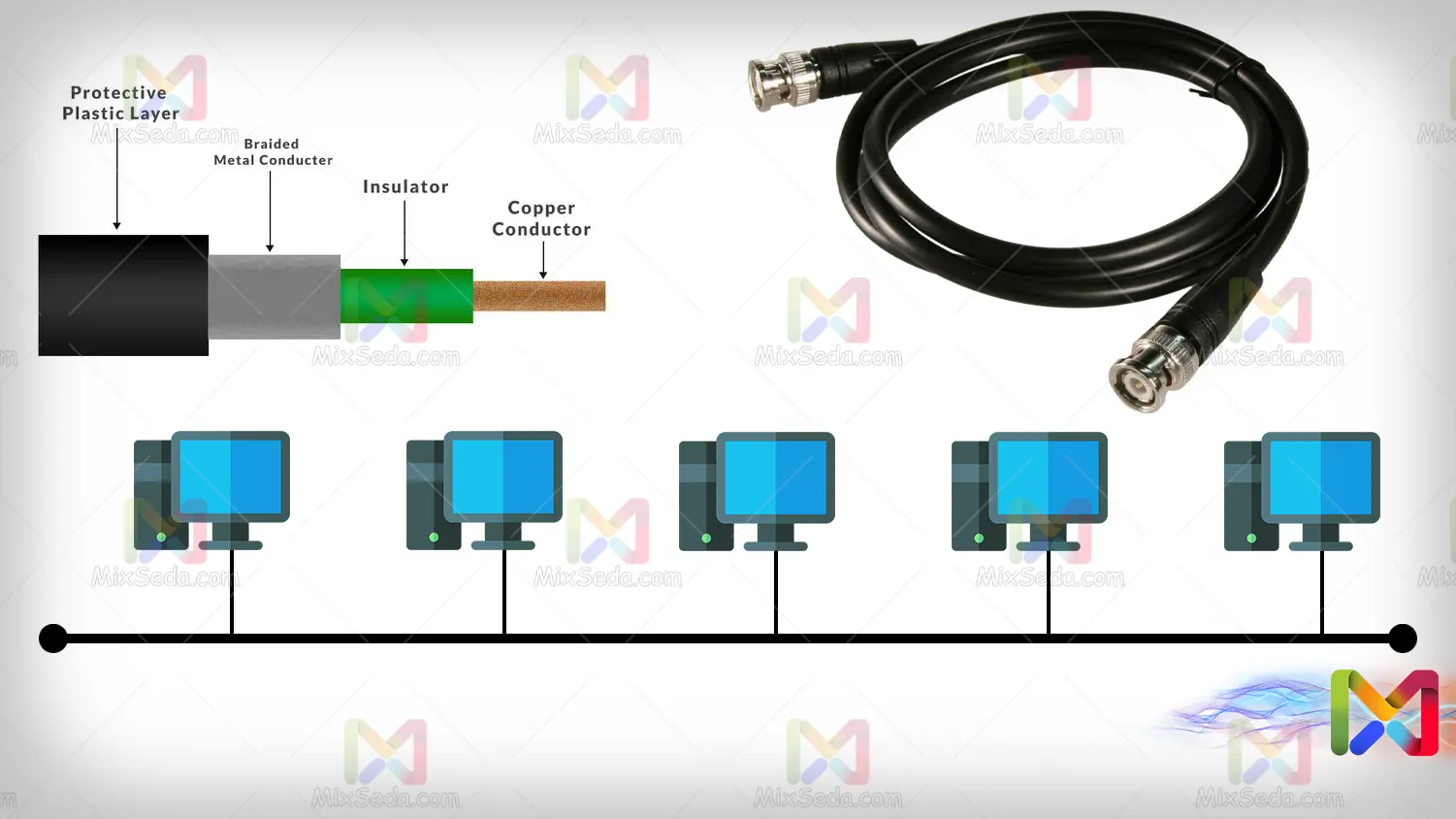
When one computer sends a packet to another computer, this packet flows through the cable and each computer receives it. So only one computer keeps this package that belongs to it and other computers release the received package.
When the packet reaches the end of the coaxial cable, one of the droppers drops all the packets.
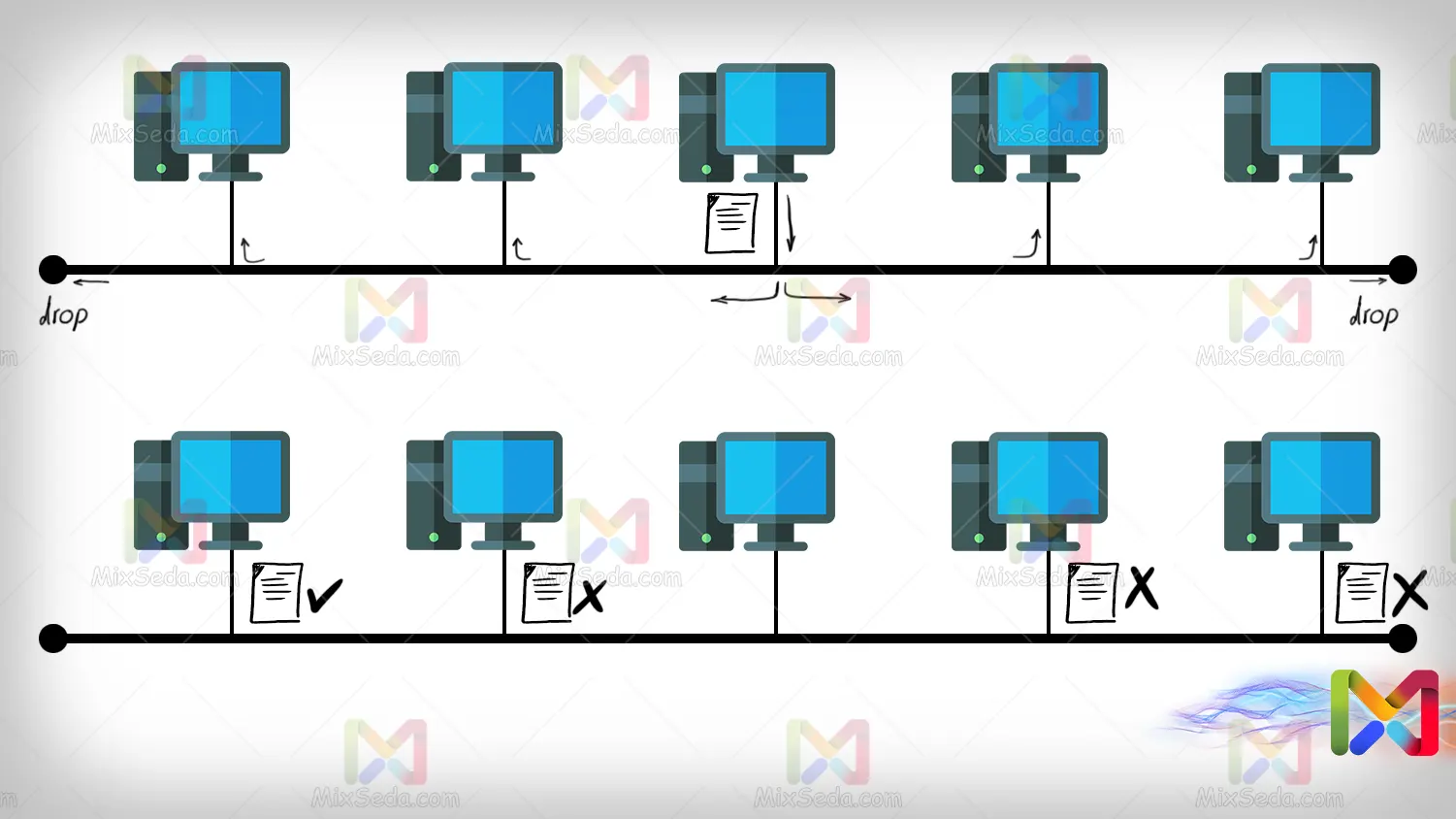
Compared to the mesh topology, the BUS topology has fewer cabling and this less cabling reduces costs. On the other hand, the expansion of networks using BUS topology is much easier than networks using mesh or ring topologies.
But in practice, we will still have a security problem in this topology because the data sent from one computer will be received by all computers.
Another disadvantage of networks using this topology is that the traffic along the cable is very high and in many cases the network slows down. On the other hand, collisions often occur in these networks.
Collision means collision or accident. When two computers start sending packets at the same time on a computer network and their sent packets go through the same path, we will see a collision.
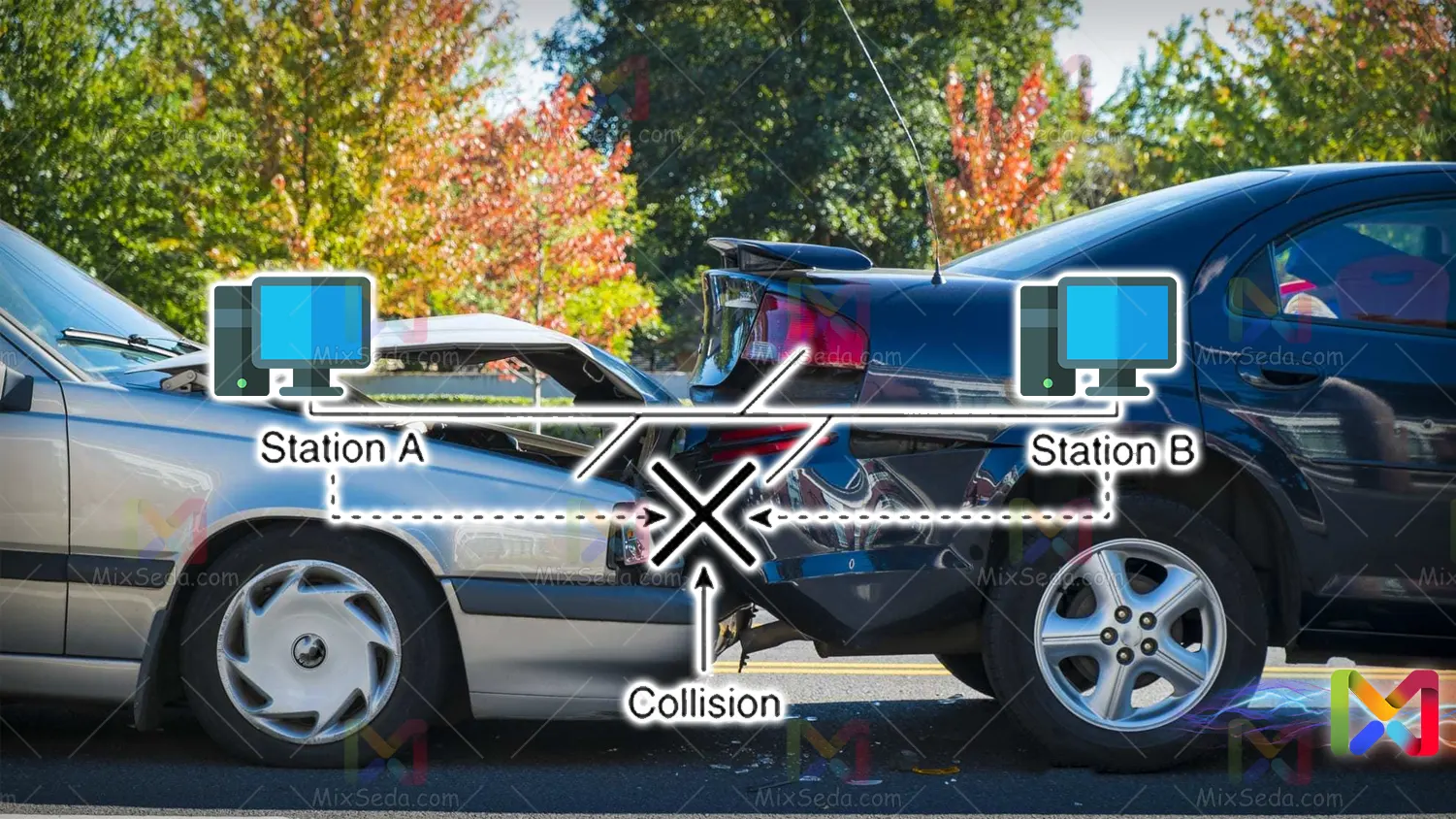
Collision in networks will cause a sharp decline in network performance. Therefore, in all technologies and products offered in the field of the network, they try to eliminate the collision or minimize the possibility of its occurrence.
The networks that use the BUS topology are of two types:
- Thick net
- Thin net
Tick net networks use thicker coaxial cables than thin net networks. In fact, the thick network network cable is of the RG-8 type and the thin network network is of the RG-58 type.
In thin mesh networks, coaxial cable is thinner and has more flexibility. In addition, RG-58 cables have an impedance of 50 ohms, which makes these cables suitable for use in BUS networks.
RG-58 cables are also used in CCTV cameras, image transmission and radio signal transmission. The standard amount of cabling in thin net networks is 185 meters maximum.
Thick mesh cables are not easily flexible and in fact these cables are thicker than thin mesh cables. The standard amount of cabling in thick mesh networks is a maximum of 500 meters.
Of course, in computer networks, the cabling is tried to be much lower than the defined standard, so that the network does not have to face communication problems in the future.
Star
The star topology is used in many computer networks today. The data throughput of this topology is much higher than other topologies and its implementation is much simpler than previous topologies.
In this topology, all workstations are connected to a central device such as a hob, switch, router or server and this central device performs the packet transmission work.
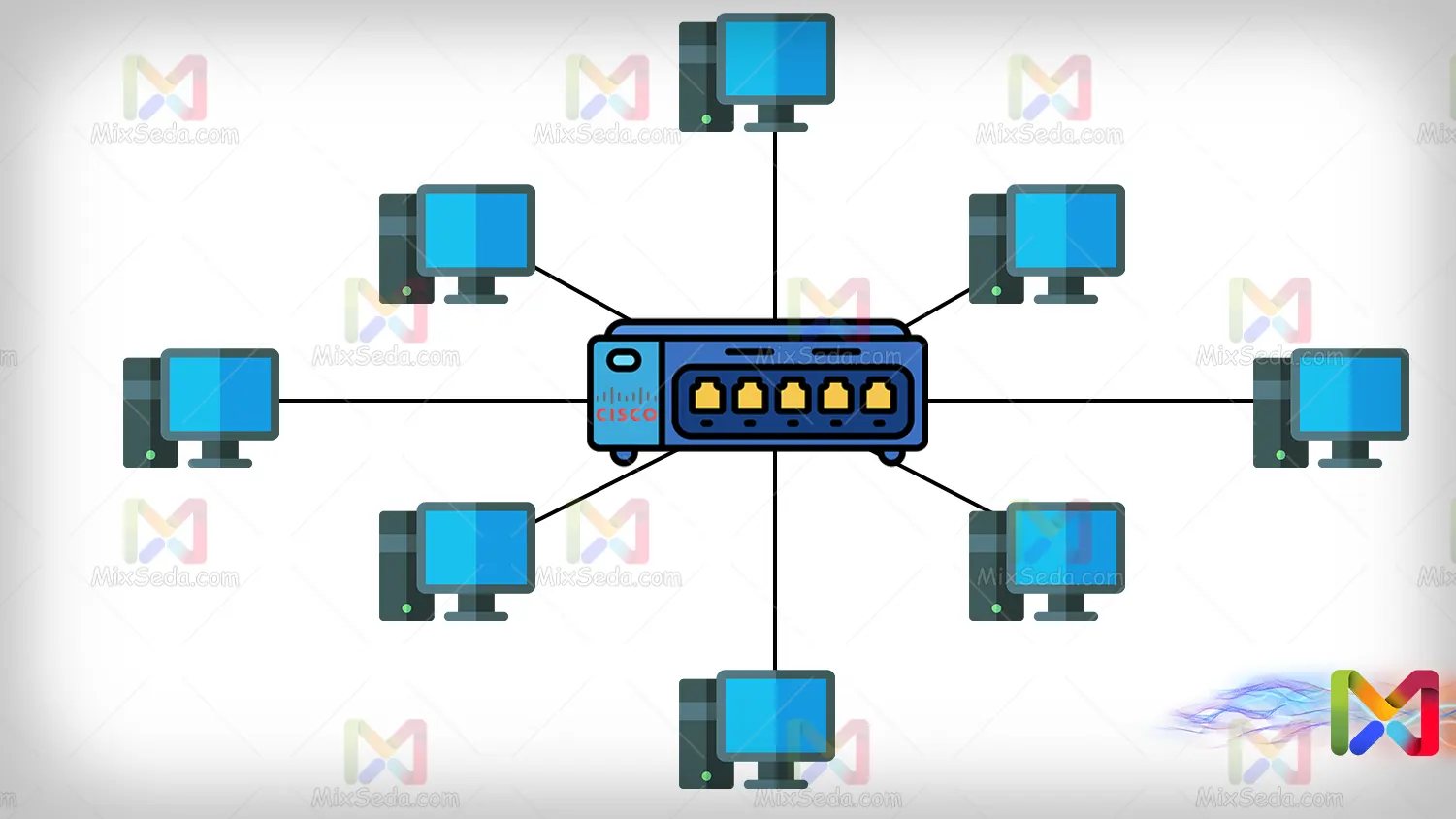
The advantages of networks using star topology are many:
- The data transfer speed is very high and this speed depends on the equipment used in the network.
- If one workstation is disconnected from the network, there will be no problems transferring data to the other workstations.
- If secure equipment is used as a central device in these networks, these networks will have high security.
- These networks are easily expandable.
- Compared to other topologies, this topology has a lower implementation cost.
- Troubleshooting networks using star topology is much easier than other topologies.
Of course, this network topology also has some disadvantages. If your central device fails, the entire network will fail as well.
Tree
The tree topology is a topology made up of several star topologies. That is, as you can see in the image below, a tree topology is formed by combining several star topologies.
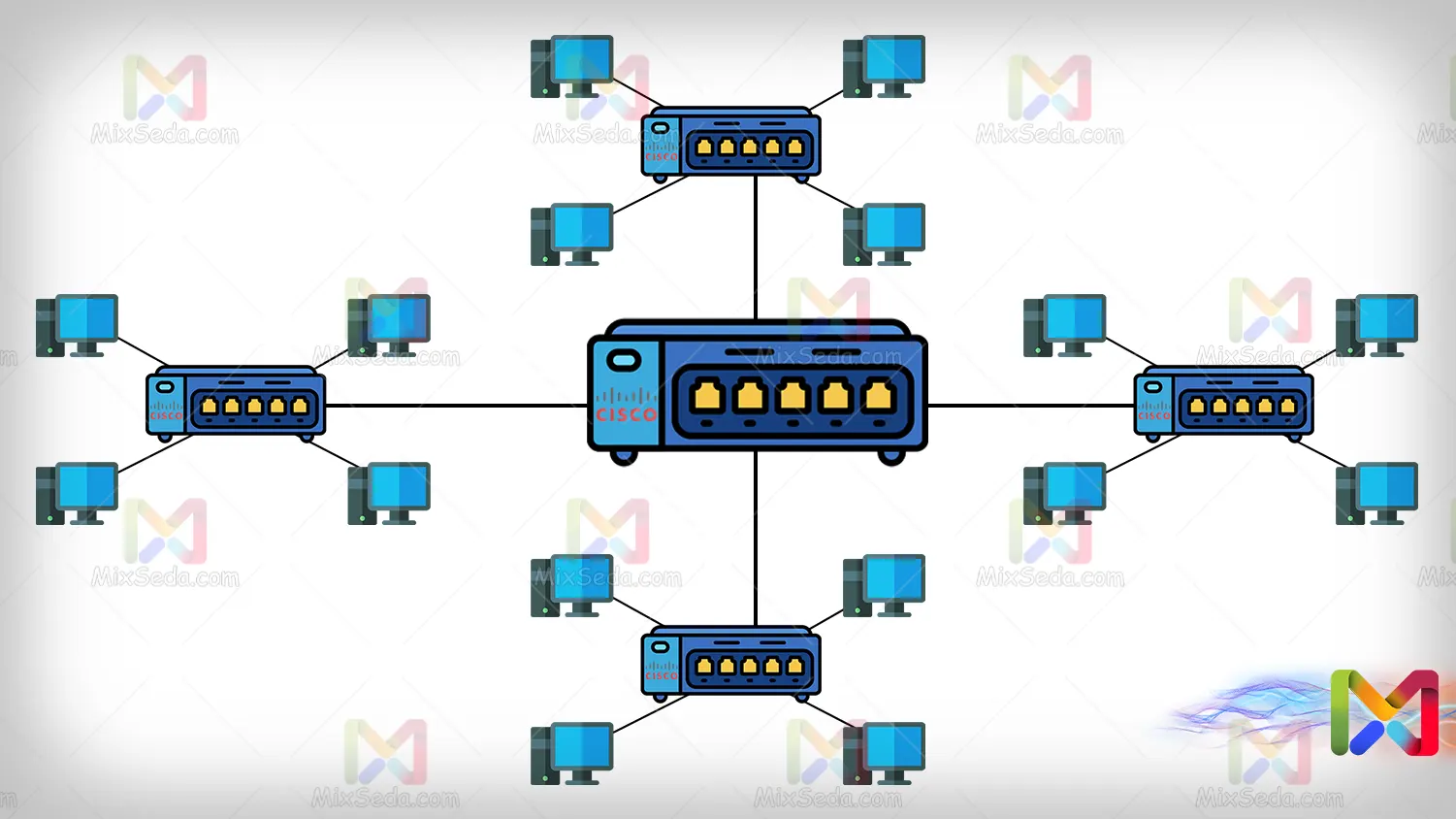
The advantages and disadvantages of networks that use Tree topology are exactly the same as Star topology.
Hybrid
Hybrid topology is a topology that uses mesh, bus, ring, and star topology. In fact, nobody uses this topology and it is mostly presented as a concept in classes.
Imagine that if ring and mesh topologies are used in a network and these two topologies are linked together using a star topology, then let's say that the topology used in this network is hybrid. Or it may be that three topologies of ring, bus and star have been used in a network and their combination is called hybrid.
In general, different scenarios for hybrid topology can be created and discussed, but what you are dealing with in today's networks is not very related to this topology and you are expected to know the structure of these topologies for knowledge only. by Network Plus.
